
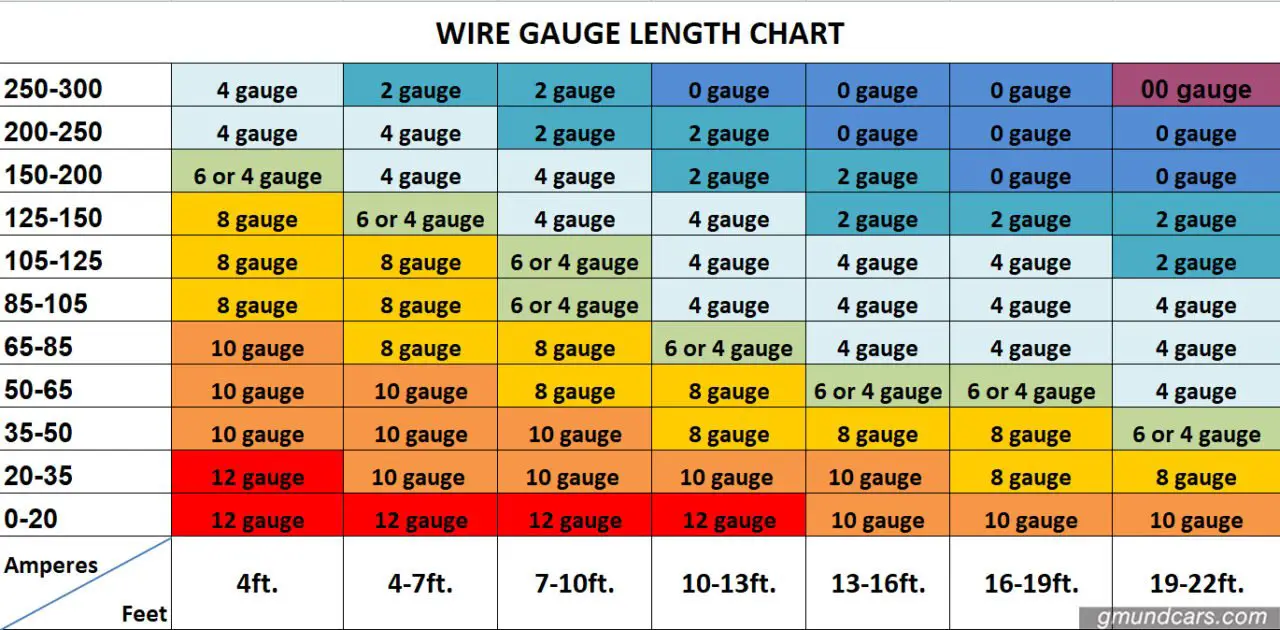
In American wire gauge, every 6-gauge decrease doubles the wire diameter, and every 3-gauge decrease doubles the wire cross sectional area. Larger wire sizes (those with a greater diameter) will have less voltage drop than smaller wire sizes of the same length. Wire size is another important factor in determining voltage drop. Copper is a better conductor than aluminum and will have less voltage drop than aluminum for a given length and wire size. Copper and aluminum are the most common materials used for wires due to their relatively low price compared with silver and gold. Silver, copper, gold, and aluminum are among the metals with the best electrical conductivity. The first is the choice of material used for the wire.

There are four major causes of voltage drop: This can be achieved by selecting the right wire, and by taking care in the use of extension cords and similar devices. It is recommended that the voltage drop should be less than 5% under a fully loaded condition. If the current is direct, the contrary pressure is called resistance.Įxcessive voltage drop in a circuit can cause lights to flicker or burn dimly, heaters to heat poorly, and motors to run hotter than normal and burn out. Impedance is a vector, or two-dimensional quantity, consisting of resistance and reactance (reaction of a built-up electric field to a change of current). If the current is alternating, such contrary pressure is called impedance. The voltage drop is the amount of electrical potential (voltage) loss caused by the contrary pressure of the wire. When electrical current moves through a wire, it is pushed by electrical potential (voltage) and it needs to surpass a certain level of contrary pressure caused by the wire.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
